The Idea
The inception and development of online marketplaces is now a rage. This is because online marketplaces have been on the rise with the growth of smartphone and related technology that is making businesses increasingly agile, with different models powering growth and revenue.
Thus, online marketplace development is something that many simply gloss over – without being equipped with a basic understanding of such a topic. This often leads to many online marketplaces being unfulfilled businesses, which might see some initial growth, but falter overtime, taking the role of stagnant, non-profitable ventures. It’s no wonder so many companies themselves are formed and die within the month.
So what draws people to online marketplace development? For starters, the size of the collaborative economy – you know this as the on-demand economy, or the sharing economy. PWC found that the size of the industry is currently at around $15 billion, and expect it to grow to $335 billion by 2025.

The marketplace economy is attracting more than 22.4 million consumers annually and $57.6 billion in spending. The largest category of marketplace spending is online marketplaces (e.g. Ebay, Etsy), with 16.3 million consumers each month spending almost $36 billion annually. Transportation (e.g. Uber, Lyft) comes in second with 7.3 million monthly consumers and $5.6 billion in annual spending, followed by food/grocery delivery (e.g. Instacart) at 5.5 million monthly consumers and $4.6 billion annual spending. Other marketplace services including home services (e.g. TaskRabbit), freelancer services (e.g. Elance), and health and beauty services (e.g. StyleSeat) account for $8.1 billion in spending each year, and all other marketplace activity comes in at $3.8 billion.
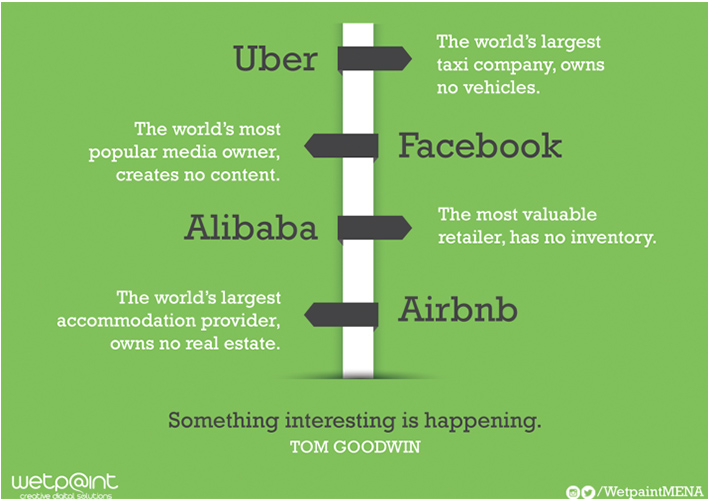
Secondly, the concept of the online marketplace itself is lucrative. Since you essentially don’t need inventory, one can indulge in online marketplace development with a potent mixture of technology, the right identification of the demand, a smooth online experience and a model that doesn’t scale up overnight, threatening to balloon the business out of proportion.
Since the online marketplace can sell anything in particular, it is important to see which sectors are trending (healthcare is particularly on the rise, for example) before engaging in marketplace development, lest you waste time and resources over an idea that sounds trendy and innovative, but is financially unviable.
Some Revenue Models
Marketplace businesses are long-term initiatives. To build a sustainable and successful marketplace, you need to find a marketplace business model that will be able to finance its operations. As online marketplaces are essentially digital platforms that match a certain set of buyers with related service providers, they make money through several ways like commissions on transactions and setting profit margins, and so on.
Most marketplaces work by charging a commission for each transaction on their platform. When a customer pays a provider, the marketplace facilitates the payment and charges either a percentage or a flat fee.
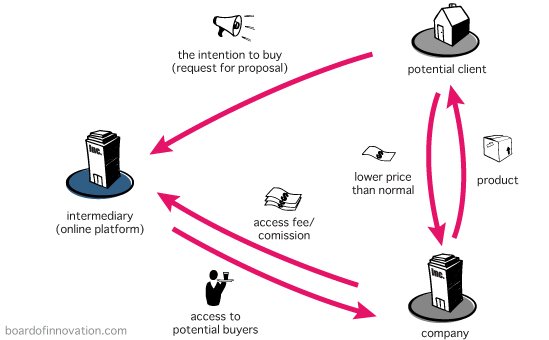
Commissions may not always work. This can be the case if the size of the typical transaction is huge, if it’s a high-luxury, or high-end service, or if the the marketplace has lots of different types of offerings which cannot all be charged the same commission. Another factor to consider would be if the marketplace does not facilitate a directly chargeable service – dating apps like Tinder would qualify.

In this case,marketplaces may charge a membership fee (sometimes called a subscription fee) where either some or all of a marketplace’s users are charged a recurring fee to access the marketplace. For example, premium users on a dating site that allows, say, a certain set of matches per day – will have access to yet other features with their premium subscription. Or take LinkedIn, which also has premium programs for greater access to workplace expertise. This is additionally called the freemium model too, where marketplaces give core offerings that are free, and compel users to take up their premium versions in order to give greater, lucrative access.
Yet other ways include listing fees (where some marketplaces charge a fee from providers when they post new listings) – this works well on sites like eBay or Craigslist. In any case, if you are not certain, trying out multiple business models, or a combination of these models to find the best option for your concept might be a good idea.
The Importance of Vision

The reason marketplace development strategies lead nowhere is also due to lack of articulation of what the business does on the entrepreneur’s part. The entrepreneur’s vision needs to be compatible with their strengths and weaknesses, along with their abilities to make said ‘dreams come true’. The marketplace development game is highly competitive precisely because of its fresh, agile nature, coupled with the promise of exponential growth in a short time period. Do not think that others aren’t looking to manipulate the same space – so what differentiates your venture from theirs? What problems are you aiming to solve with extant sectors, such that you might disrupt them? Why should users engage in your marketplace? Your professional experience, education, initial contacts and financial resources will determine the answers to many of these questions.

More importantly, do you have any idea as to what the status of your Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is? Do you know what this concept is? Research and knowledge as concerns marketplace development is also key – blindly jumping in is a bad idea. Having an MVP basically means you have a working model of your marketplace without it being commercially released and being determined a failure right off the bat. If your MVP doesn’t work out, at least you can work on your idea more, honing it, and then getting it ready for deployment rather than wasting additional time and resources in a potentially loss-making idea. It’s a prototype that will save you from your sins, essentially.

Lastly, an important part of your marketplace development plan are the users. Interacting with your users as soon as you start working on your project is absolutely crucial, in addition to having an MVP, where they act as buffers to your idea going wild and giving you a ground-level understanding of their needs and wishes as pertains to your idea. The ones who are truly successful make sure to engage their users at every point along the way in order to solve bigger and bigger problems by presenting transformative solutions to the way we live our lives.






